کامپیوتر، شبکه
کپی برداری از مطالب وبلاگ با ذکر منبع مجاز است.
Ubuntu 20.04 SSH Server
دوشنبه نهم اسفند ۱۴۰۰ 11:28In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to install SSH Server
- How to change SSH server’s status
- How to open firewall rules to allow SSH incoming traffic
- How to connect to SSH Server remotely using the ssh command
- How to change default SSH listening port
Ubuntu 20.04 SSH Server
Software Requirements and Conventions Used
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | Installed Ubuntu 20.04 or upgraded Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa |
| Software | OpenSSH |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
Ubuntu 20.04 SSH Server step by step instructions
- Install the openssh-server in order to perform an installation of the SSH server on your Ubuntu 20.04 system:
$ sudo apt install openssh-server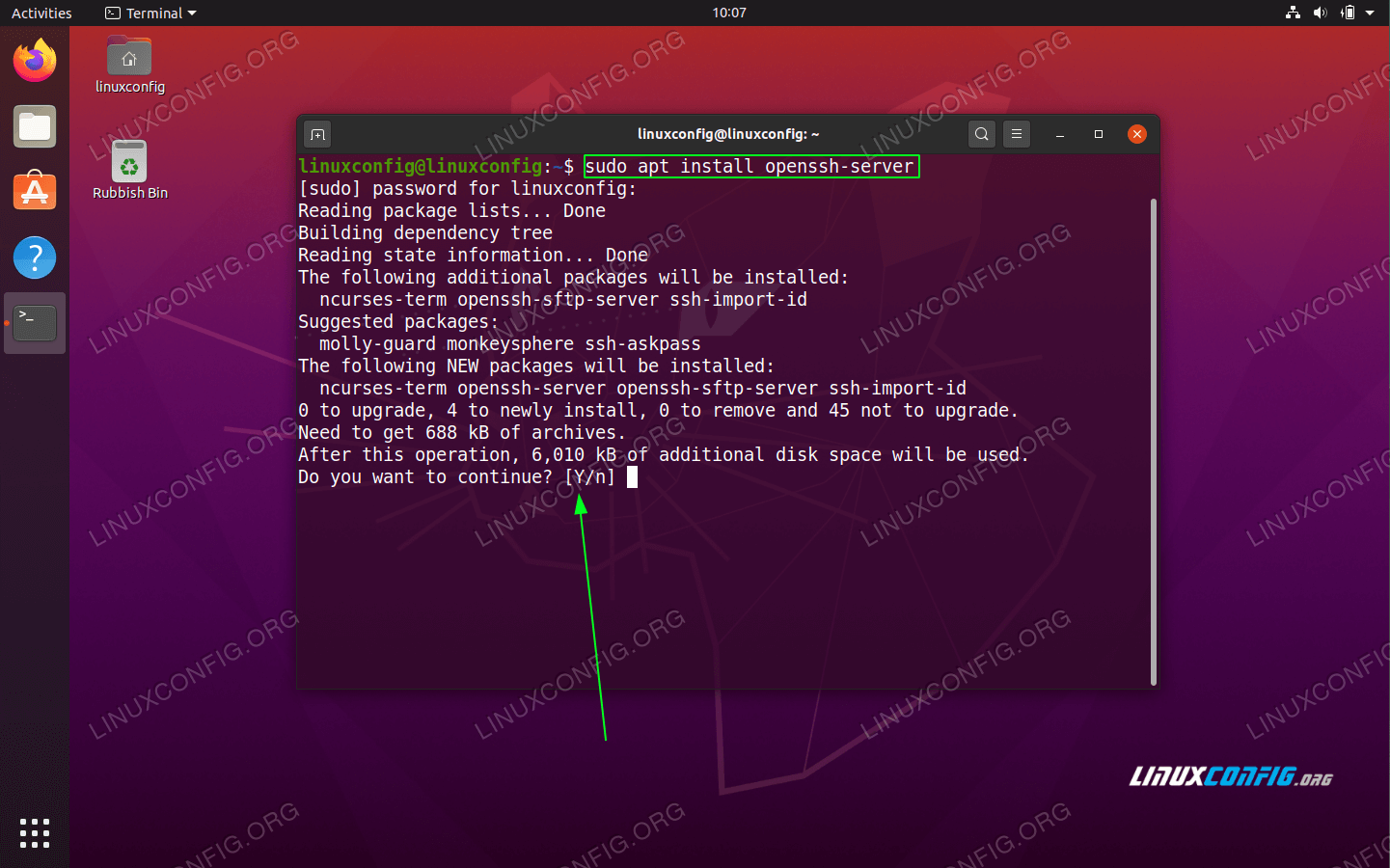
OpenSSH server installation on Ubuntu 20.04 Server/Desktop
- Check the status. After the SSH server package installation the SSH server daemon should be up and running. To check the status of your SSH server execute the following command:
$ systemctl status sshd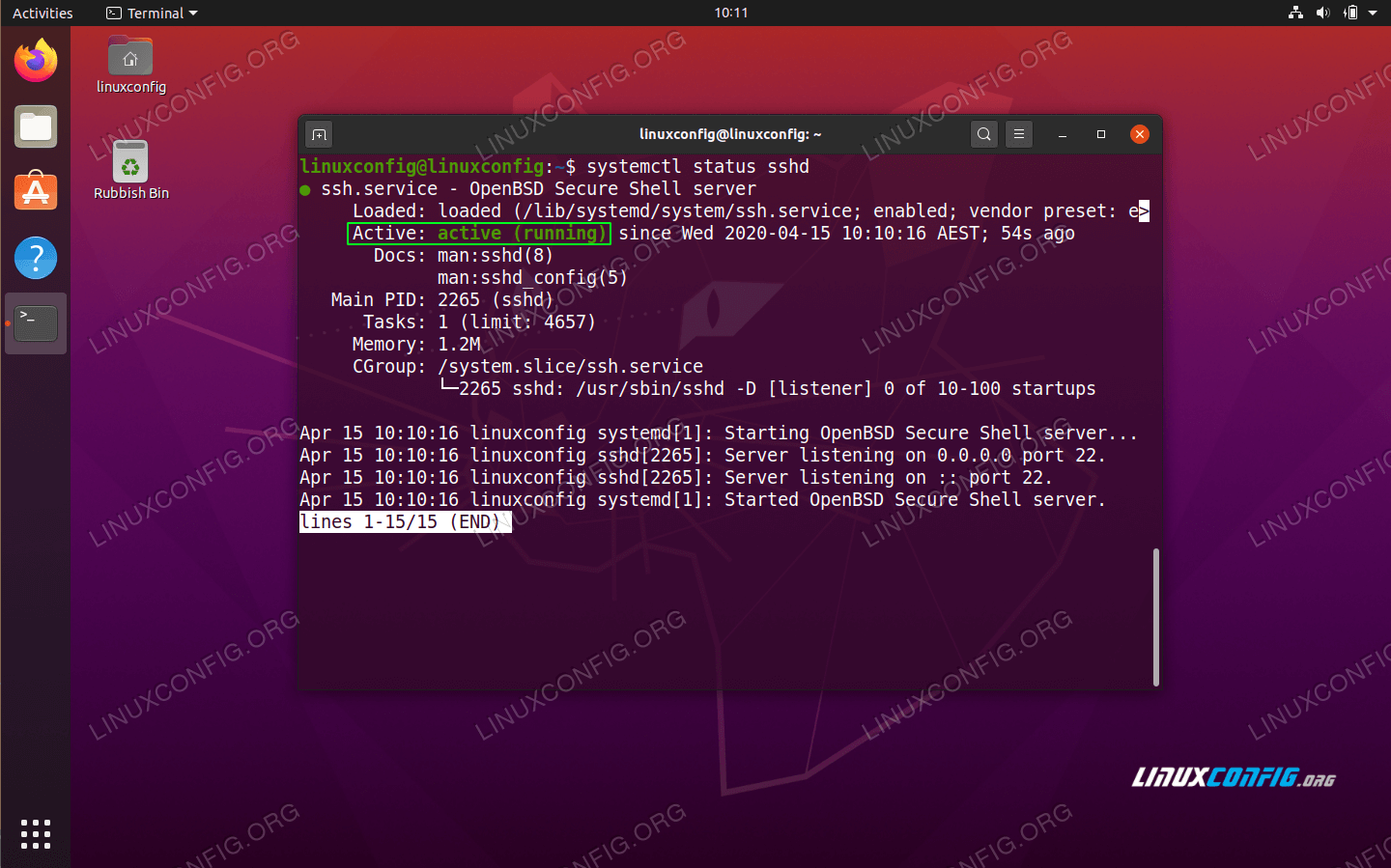
Check the SSH server status. Press q to quit the status page.
To start, stop and restart your SSH server use the systemctl command. For example the below command will restart the SSH server daemon:
$ sudo systemctl restart ssh - Open ssh port 22 for an incoming traffic on your firewall:
$ sudo ufw allow ssh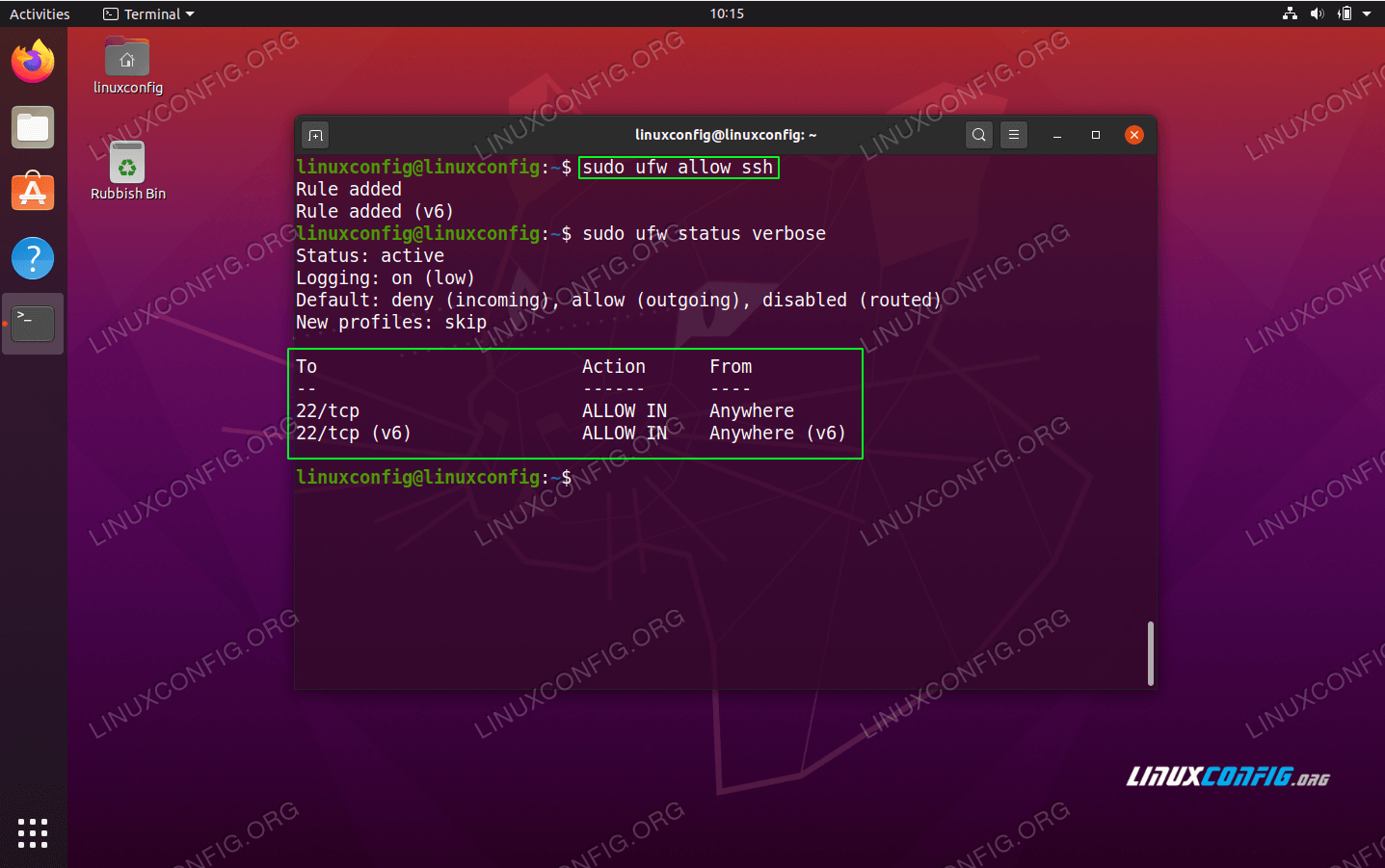
Open SSH port 22 and check the firewall status
- Enable the SSH server to start automatically during the boot.
$ sudo systemctl enable ssh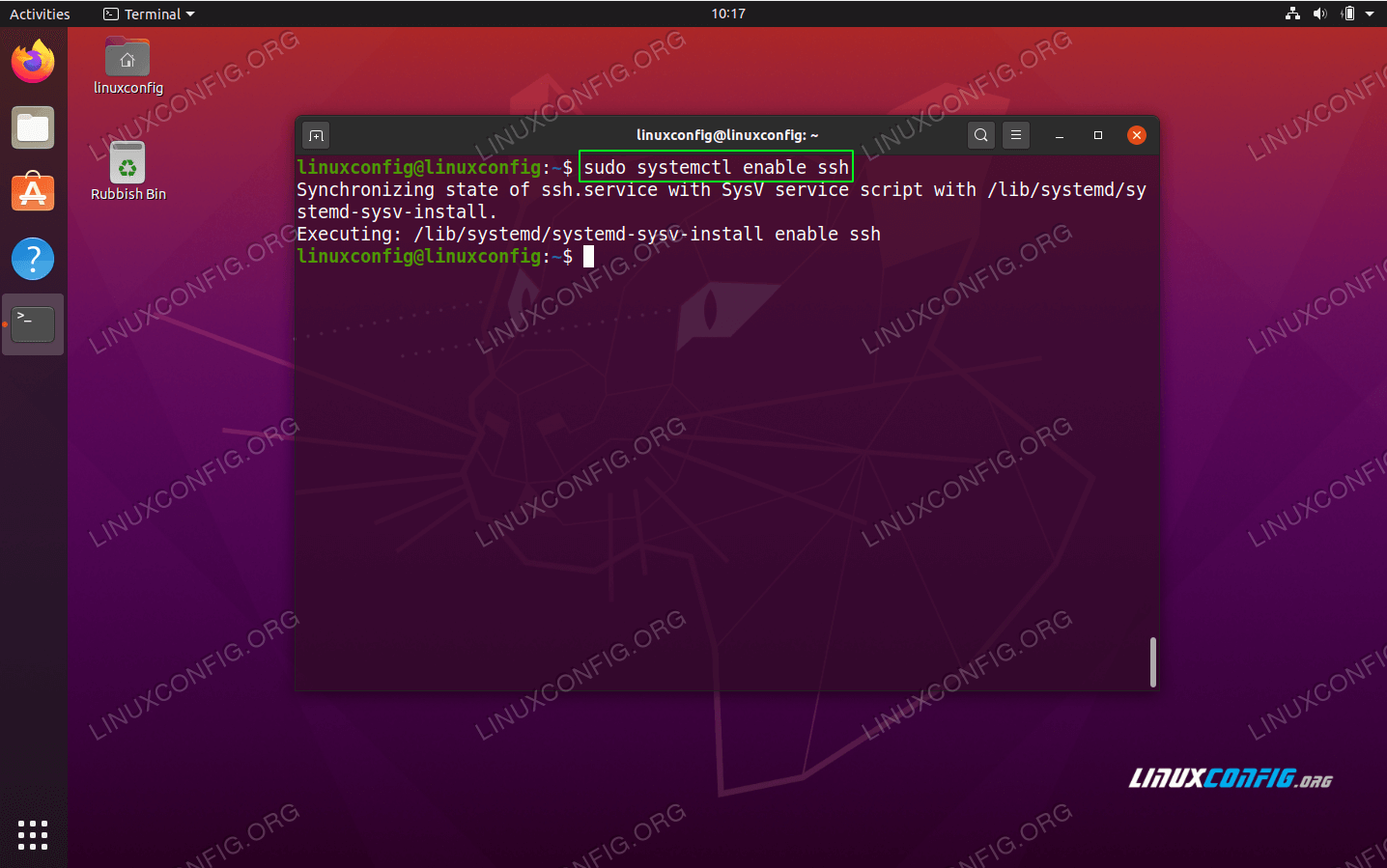
Ensure the SSH Server on your Ubuntu 20.04 system start after reboot
- Connect from a remote client to your SSH server. First, obtain an IP address of your SSH server. To do so execute the bellow ip command:
$ ip aIn case you wish to connect to your SSH server over the internet you well need to obtain your external IP address:
$ echo $(wget -qO - https://api.ipify.org)
Obtain a local IP address by using the ip command.
Lastly, connect to your SSH server remotely using the following ssh command syntax ssh username@hostname-or-ip-address.
For example the bellow command will connect to the Ubuntu 20.04 SSH server with an IP address 192.168.1.112 as a user linuxconfig:
$ ssh linuxconfig@192.168.1.112
Connecting to SSH server remotely. For a first time connection you will need to accept ssh fingerprint by typing yes.
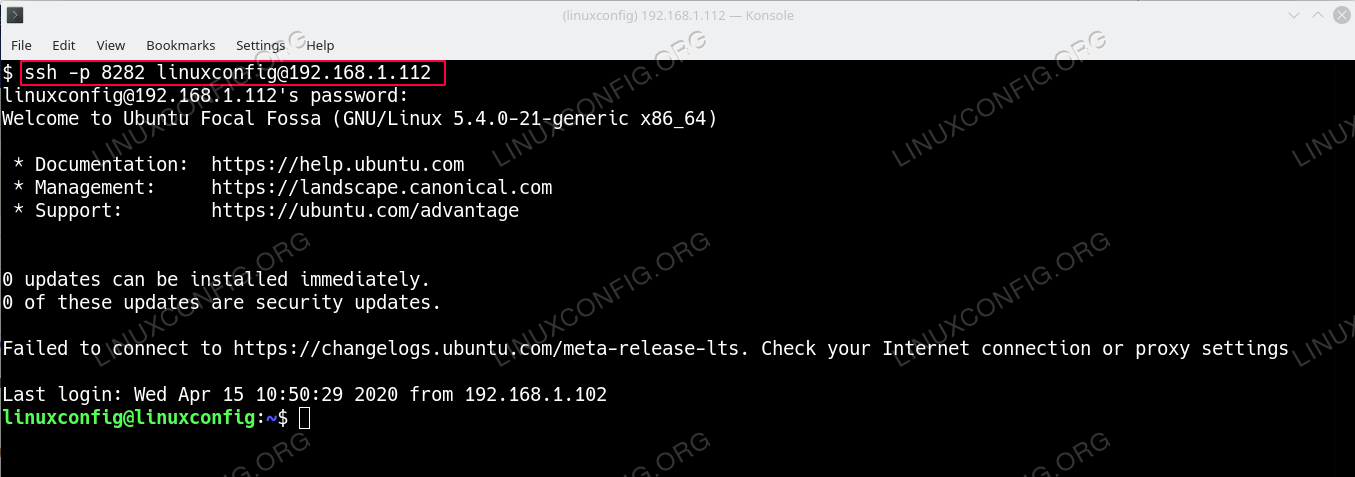
- (optional) From security reasons it is recommended to change the default SSH port 22 to some other arbitrary port number above 1024. To do so edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config configuration file as an administrative sudo user.
For example to change the defalut SSH port number from 22 to eg. 8282 add the following line into the SSH config file:
Port 8282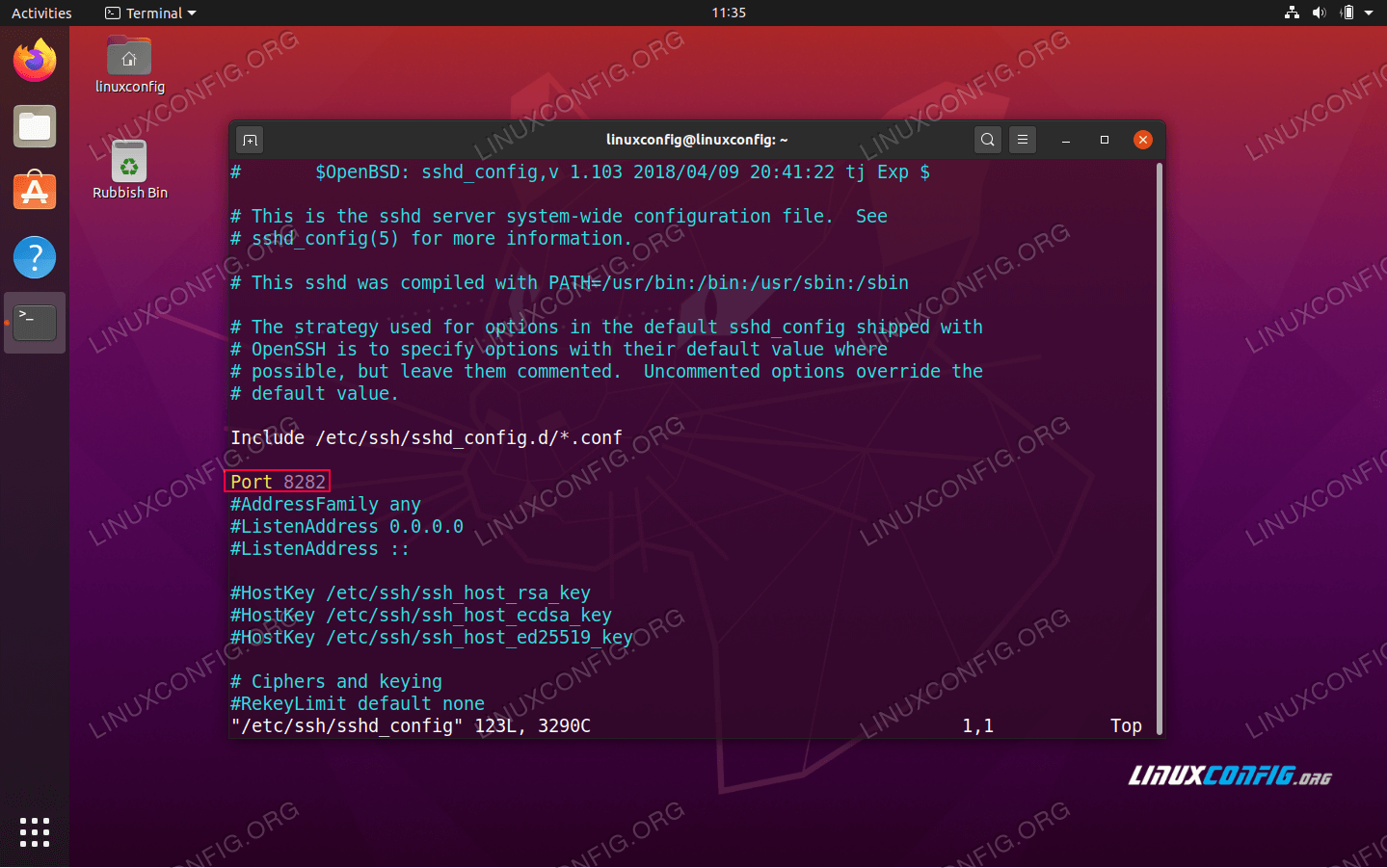
Changing the default SSH port number via /etc/ssh/sshd_config SSHD configuration file.
Once you have made the appropriate change open a firewall port to correspond with the new SSH port:
$ sudo ufw allow 8282/tcpTo apply the change to your SSH server use systemctl command to restart it:
$ sudo systemctl restart sshIn order to remotely connect to a specific SSH Server port number use the -p ssh command line option. Example:
$ ssh -p 8282 linuxconfig@192.168.1.112 source